1991. Maximum flow
Find the maximum flow in the given network.
Input. The first line contains two integers n and m
(1 ≤ n ≤ 100, 1 ≤ m ≤ 10000) –
respectively the number of vertices and edges in the network. Each of the
following m lines contains three numbers ui, vi
and ci (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤
n, 1 ≤ ci ≤ 10000), meaning that between
vertices ui and vi in the network there is
an edge with capacity ci. Vertex 1 is the source, and the
vertex n is the destination. Graph of the network is undirected and can
contain multiple edges. All numbers are integers.
Output. Print the maximum flow in the given network.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
3 31 2 31 3 5
3 2 7 |
8 |
SOLUTION
graph – maximum flow
Algorithm analysis
In this problem it is enough to
implement the algorithm of finding the maximum flow in the undirected graph with multiedges. For example,
to find the augmenting path from source
to
destination, we’ll use the depth first search.
Example
The graph from the test case has the
following form. The source is shown in green and the destination in orange.
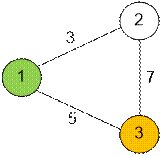
Algorithm realization
The weights of
the graph edges are stored in the matrix m. In the array used we mark the used
vertices during the depth first search.
#define MAX 120
int m[MAX][MAX], used[MAX];
The AugPath(vCur,
Final, CurFlow) function finds the residual capacity of the augmenting path from vCur
to Final if the residual capacity of the augmenting path from the
start vertex to vCur equals to CurFlow.
int AugPath(int
vCur, int Final, int
CurFlow)
{
if (vCur ==
Final) return CurFlow;
if
(used[vCur]++) return 0;
for (int Flow, To = 1; To <= n; To++)
{
Consider an edge (vCur, To).
if
(m[vCur][To] > 0 &&
(Flow =
AugPath(To,Final,min(CurFlow,m[vCur][To]))))
{
m[vCur][To] -= Flow; m[To][vCur] += Flow;
return
Flow;
}
}
return 0;
}
The main part of
the program. Read the input
data. If the graph contains multi-edges between vertices a and b
with capacities ñ1, ñ2,
…, ck, then we assume that there is one edge between a
and b with capacity ñ1 + ñ2 + … + ck.
scanf("%d %d",&n,&Edges);
memset(m,0,sizeof(m));
while (Edges--)
scanf("%d %d
%d",&a,&b,&c), m[a][b] += c, m[b][a] += c;
As long as there is an
augmenting path, increase the flow amount MaxFlow between
source 1 and sink n.
MaxFlow = 0;
do
{
memset(used,0,sizeof(used));
} while ((flow = AugPath (1,n,0x7FFFFFFF)) &&
(MaxFlow += flow));
Print the maximum flow.
printf("%d\n",MaxFlow);
Algorithm realization – Edmonds - Karp
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#define MAX 120
#define INF 2000000000
using namespace
std;
int m[MAX][MAX], used[MAX], parent[MAX];
int a, b, c, flow, MaxFlow, n, Edges;
void bfs(int
v)
{
queue<int>
q;
q.push(v); used[v] = 1;
while(!q.empty())
{
int from =
q.front(); q.pop();
if (from
== n) return;
for(int to = 1; to <= n; to++)
if
((m[from][to] > 0) && (!used[to]))
{
used[to] = 1;
parent[to] = from;
q.push(to);
}
}
}
void Rebuild(int
k, int flow)
{
if (parent[k]
== -1) return;
Rebuild(parent[k],flow);
m[parent[k]][k] -= flow;
m[k][parent[k]] += flow;
}
int FindFlow(int
k)
{
if (parent[k]
== -1) return INF;
int x =
FindFlow(parent[k]);
return
min(x,m[parent[k]][k]);
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d
%d",&n,&Edges);
memset(m,0,sizeof(m));
while
(Edges--)
{
scanf("%d
%d %d",&a,&b,&c);
m[a][b] += c; m[b][a] += c; // multiedges
}
MaxFlow = 0;
while(1)
{
memset(parent,-1,sizeof(parent));
memset(used,0,sizeof(used));
bfs(1);
flow
= FindFlow(n);
if (flow ==
INF) break;
MaxFlow += flow;
Rebuild(n,flow);
}
printf("%d\n",MaxFlow);
return 0;
}
Algorithm realization – Dinic
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#define MAX 120
#define INF 0x3F3F3F3F
using namespace
std;
int Cap[MAX][MAX], CurFlow[MAX][MAX],
used[MAX], d[MAX],
q[MAX], ptr[MAX];
int a, b, c, MaxFlow, n, Edges;
int min(int
i, int j)
{
return (i
< j) ? i : j;
}
int bfs(int
s)
{
int qh =
q[qt++] = s;
memset (d, -1, sizeof(d));
d[s] = 0;
while (qh
< qt)
{
int v =
q[qh++];
for (int to = 1; to <= n; to++)
if ((d[to]
== -1) && (CurFlow[v][to] < Cap[v][to]))
{
q[qt++] = to;
d[to] = d[v] + 1;
}
}
return d[n]
!= -1;
}
int dfs(int
v, int flow)
{
if
(!flow) return
0;
if (v ==
n) return
flow;
for (int &to = ptr[v]; to <= n; to++)
{
if (d[to]
!= d[v] + 1) continue;
int pushed
= dfs (to, min (flow, Cap[v][to] - CurFlow[v][to]));
if (pushed)
{
CurFlow[v][to] += pushed;
CurFlow[to][v] -= pushed;
return
pushed;
}
}
return 0;
}
int Dinic(int
s)
{
int flow = 0;
for (;;)
{
if (!bfs(s)) break;
memset(ptr,0,sizeof(ptr));
while (int pushed = dfs (s, INF))
flow += pushed;
}
return flow;
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d
%d",&n,&Edges);
memset(Cap,0,sizeof(Cap));
memset(CurFlow,0,sizeof(CurFlow));
while
(Edges--)
scanf("%d %d %d",&a,&b,&c),
Cap[a][b] += c, Cap[b][a] += c;
MaxFlow = Dinic(1);
printf("%d\n",MaxFlow);
return 0;
}
